Written by our Talents, published on medium.com/d-one
-

The Power of Connections: Accelerating Data Deduplication
As organizations accumulate data across disparate systems, duplicates emerge due to inconsistent standards and fragmented processes. The article reframes deduplication as a strategic capability rather than a cleanup task. It introduces a holistic framework that combines business rules with technical methods. Central to this is modeling records as connected nodes in a graph, enabling scalable identification of duplicate clusters instead of relying solely on pairwise comparisons. Coupled with standardized data preparation, clear business definitions of what constitutes a duplicate, and principled “survivorship” rules to select the golden record, this approach ensures higher data quality. The process becomes modular, scalable, and robust—even for large, evolving datasets.
Technical Keywords
- Data Deduplication
- Record Linkage
- Graph-Based Clustering
- Connected Components
- Data Survivorship / Golden Record
- Blocking & Similarity Metrics (e.g., Levenshtein) -

Self-Healing Data Governance with Databricks: Auto-Reverting Unauthorized Permission Changes
Modern data platforms often struggle with permission drift — when access rights for data assets change outside of approved processes, risking data security and compliance. The article describes an approach to build a self-healing governance mechanism on top of Unity Catalog in Databricks, which automates the detection of unauthorized permission changes and reverts them to the last known good state. It combines audit-log monitoring, policy-as-code definitions of desired permission states, and automated workflows (via Terraform, Python, etc.) that enforce and restore correct permissions. In effect, the system continuously detects → evaluates → reverts undesirable permission changes, thereby maintaining governance guardrails without depending solely on manual reviews.
Technical Keywords
- Permission Drift
- Unity Catalog (Databricks)
- Policy-as-Code, Infrastructure as Code
- Domain-Oriented Ownership
- Automated Monitoring & Remediation
- Audit Logs & Access Control -
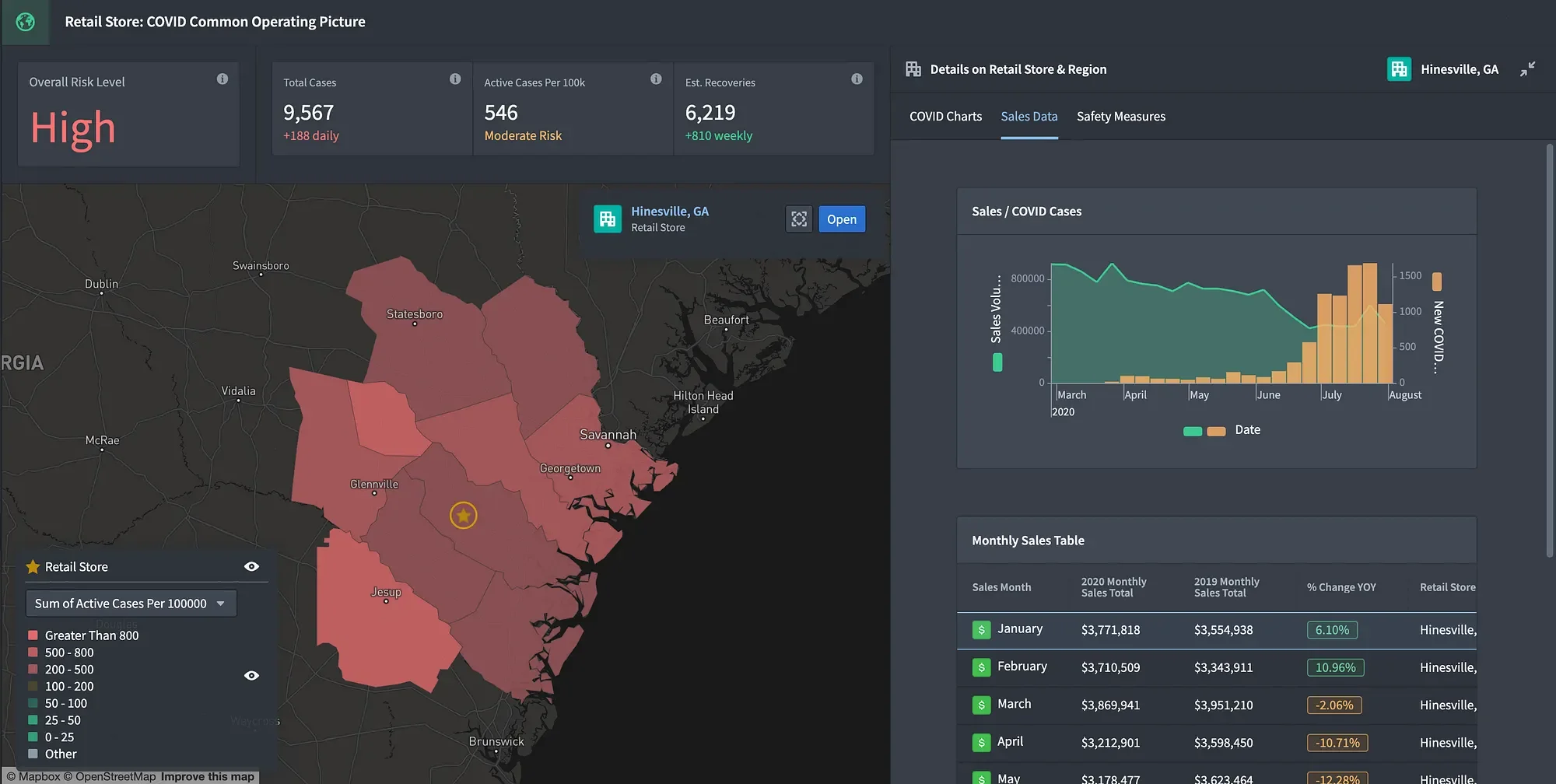
Mastering Palantir Foundry Workshop: Building Insightful Dashboards
As static BI increasingly falls short for real-time operational insight, organisations need dashboards that behave more like applications. The article explains how Palantir Foundry’s Workshop enables the construction of such interactive dashboards. It walks through building a logistics “shipment” dashboard by defining pages and sections, configuring widgets like object tables, charts, and filters, and linking them through variables and object sets. Interactivity is driven by events and reactive logic, allowing user selections to dynamically update all connected components. By modelling shipments within the Ontology and wiring components in Workshop, the resulting dashboard becomes a responsive interface for exploring inbound and outbound logistics data
Technical Keywords
- Palantir Foundry Workshop
- Object Types & Ontology Modelling
- UI Layout
- Object Set Filtering
- Event-Driven Interactivity
- Reactive Dashboard Logic
-
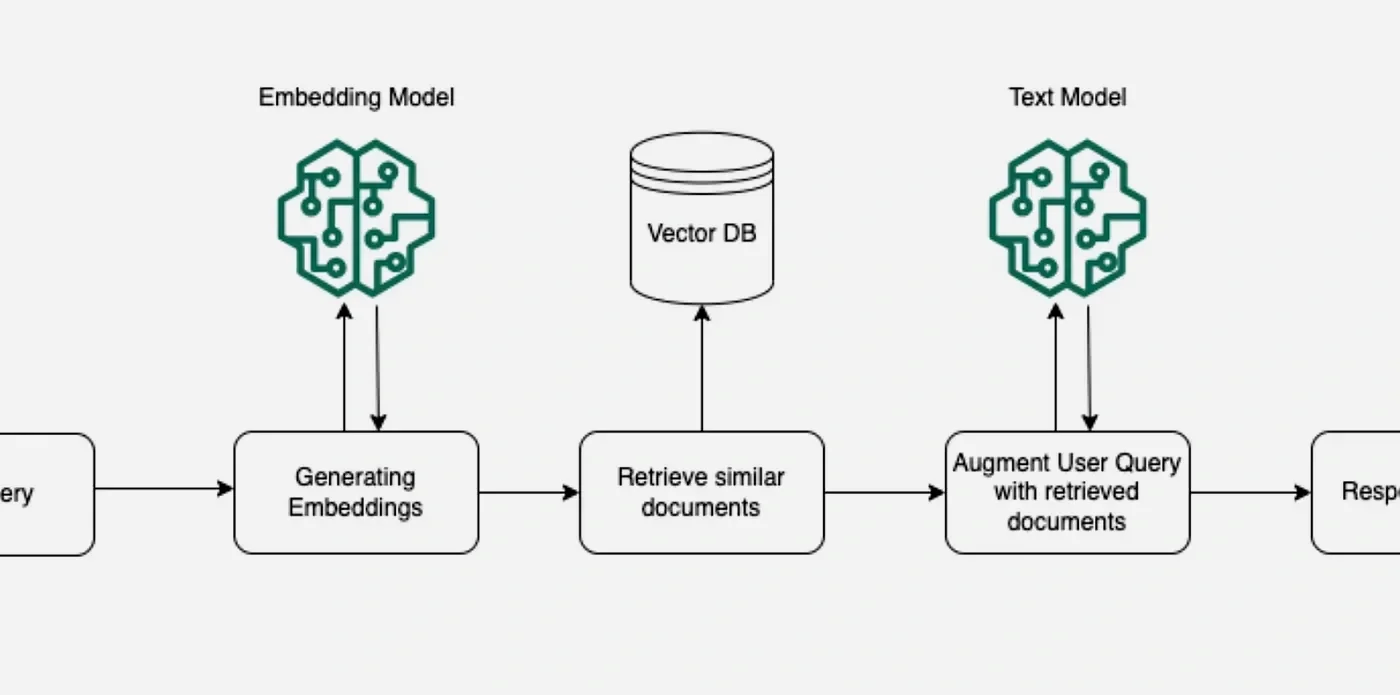
A Design Guide for RAG Engineering on AWS using Bedrock Knowledge Bases
As the adoption of generative AI grows (over 70% of companies use LLMs as of 2025), the demand for scalable and efficient RAG solutions increases. This article offers a practical design guide for building Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) systems on AWS using Amazon Bedrock Knowledge Bases. It covers key aspects such as data preprocessing, embedding, prompt routing, source attribution, and monitoring – all focused on enabling fast transitions from prototype to production with minimal engineering overhead.
Technical Keywords
- Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG)
- Amazon Bedrock Knowledge Bases
- Embedding & Vector Search
- Intelligent Prompt Routing
- Bedrock Data Automation
- Monitoring & Observability -

Think in Services, Deliver as Products: The New Data Mesh Mindset
As data platforms grow in complexity, traditional centralized architectures no longer suffice. The article introduces Data Mesh, a paradigm that decentralizes responsibility to domain-oriented teams. It emphasizes the shift from monolithic pipelines to modular Data Services, each encapsulating the full lifecycle of a data product—from ingestion and transformation to deployment, monitoring, and governance. These services are self-contained, composable, and domain-owned, enabling scalable, high-quality data delivery
Technical Keywords
- Data Mesh
- Data Services
- Data Products
- Domain-Oriented Ownership
- Lifecycle (Ingestion → Deployment → Monitoring)
- Modular & Composable Architecture -

Analyze multilingual customer feedback: Superbe séjour — Ospiti piacevoli — Wir kommen wieder!
Switzerland’s multilingual customer feedback—often submitted in German, French, or Italian—poses challenges for scalable analytics. The authors demonstrate how Microsoft Fabric enables a unified, end-to-end pipeline spanning raw data ingestion, translation (via SynapseML), sentiment analysis, and visualization in Power BI.
The result is a scalable, automatic multilingual reporting solution that uncovers region-specific customer insights.
Technical Keywords
- Multilingual text ingestion & processing
- Microsoft Fabric (OneLake, PySpark, SynapseML)
- Machine translation + Dual sentiment analysis
- Power BI (word clouds, geospatial dashboards)
- Automated analytics pipeline

